scientists of the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) developed a technology for producing alkali-activated bricks/blocks by utilising fly ash and furnace slag.
Key Highlights
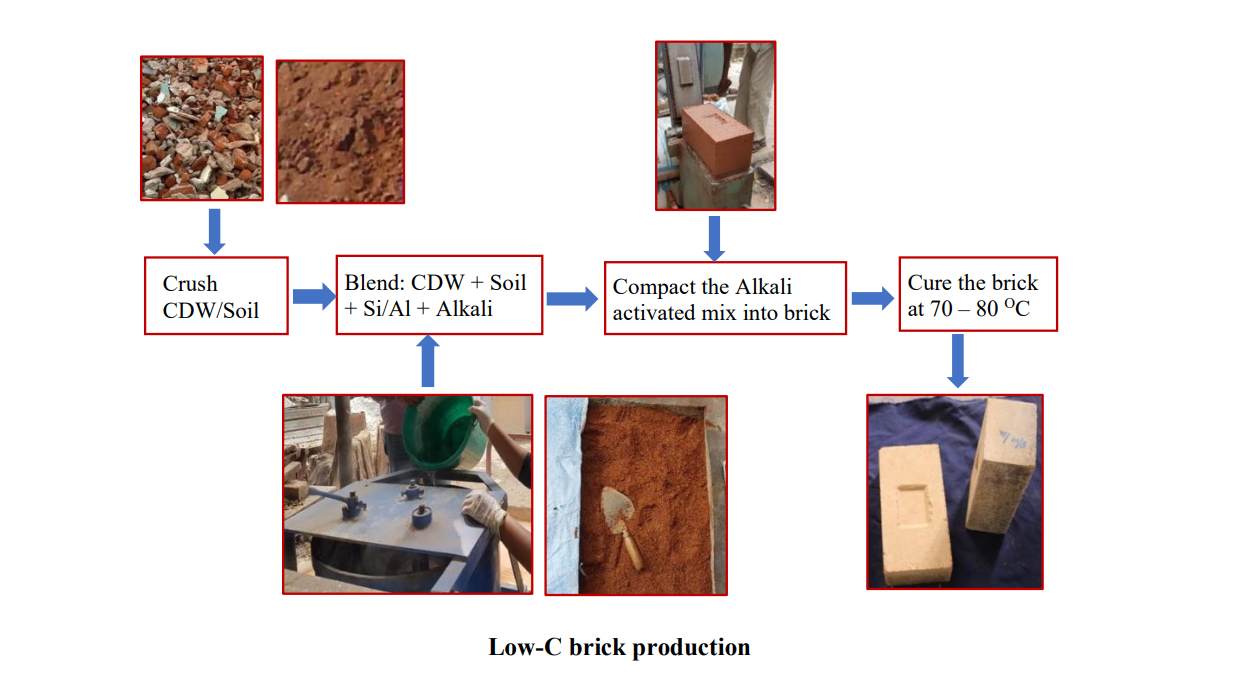
- Researchers have devised a technique that uses construction and demolition waste (CDW) and alkali-activated binders to create energy-efficient walling materials.
- These low-carbon (low-C) bricks don’t need to be fired at high temperatures, and they don’t need high-energy components like Portland cement.
- The construction industry in general, and the building sector in particular, will be the primary beneficiaries of this progress.
- The Department of Science and Technology provided funding for the project.
The team of researchers developed low embodied carbon bricks from CDW waste through an alkali activation process using fly ash and ground slag and characterising the thermal, structural, and durability characteristics of Low-C bricks and their masonry. After ascertaining the Physico-chemical and compaction characteristics of the CDW, the optimum mix ratios of the materials were obtained, and then the production process was evolved to produce low-C bricks. Based on the optimum binder proportions, the compressed bricks were manufactured. The bricks were examined for engineering characteristics.
The major beneficiary of this development undertaken by IISc Bangalore with funding from the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, is the construction industry in general and the building sector in particular. This technology will also mitigate the disposal problems associated with the C&D wastes.
