The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope developed by NASA with contributions from the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The telescope is named after James E. Webb, who was the administrator of NASA from 1961 to 1968 and played an integral role in the Apollo program.
It is intended to succeed the Hubble Space Telescope as NASA's flagship mission in astrophysics. JWST was launched 25 December 2021 on Ariane flight VA256. It is designed to provide improved infrared resolution and sensitivity over Hubble, viewing objects up to 100 times fainter and will enable a broad range of investigations across the fields of astronomy and cosmology, including observations up to redshift z≈20 of some of the oldest, most distant, events and objects in the Universe such as the first stars and formation of the first galaxies, and allowing detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets.
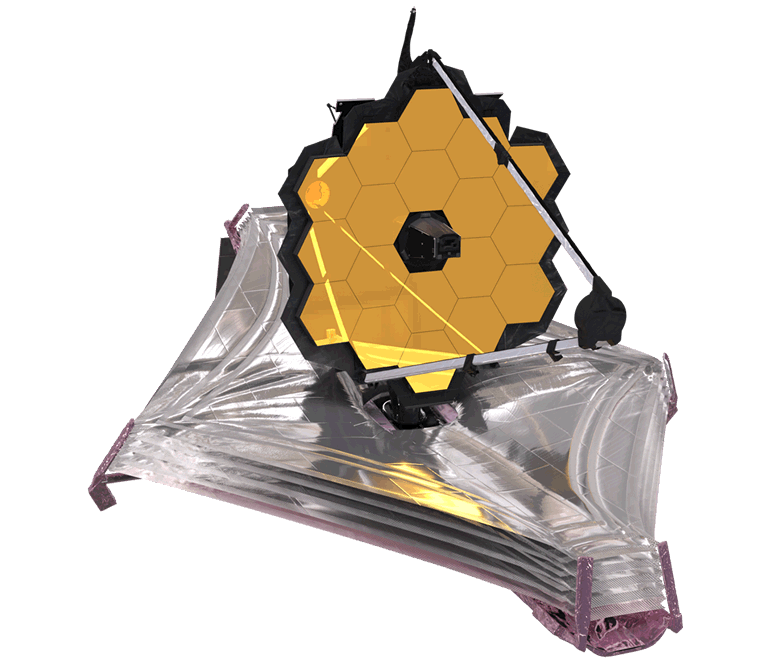 |
| James Webb Space Telescope |
What is the size of web mirror?
Webb’s segmented primary mirror has a diameter of 6.6 meters (21.7 feet). Each of the 18 segments is 1.32 meters (4.3 feet) across. The area of the mirror is approximately 25 square meters (270 square feet) and the mass is 705 kilograms (1,550 pounds on Earth).How big is the webb telescope?
The sunshield dimensions are 21.2 by 14.2 meters (69.5 by 46.5 feet) and the height of the entire observatory is 8 meters (28 feet).Why does webb need a sunshield?
To accurately and precisely detect faint infrared light from distant objects in the universe, Webb must be shielded from the strong infrared light emanating nearby from the Sun, Earth, and Moon. The sunshield’s five layers block the light from these nearby objects.What is the expected lifespan of the webb telescope?
Webb is designed to have a minimum five years of science operations, with the goal of having an overall mission lifetime greater than 10 years.Which instruments are on the webb telescope and what do they do?
Webb has four scientific instruments, the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), the Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS), and the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI). Each of these instruments uses infrared detectors to capture light from distant astronomical sources.How is webb powered?
The Webb telescope is powered by an on-board solar array. It also has a propulsion system to maintain the observatory’s orbit and attitude. The solar array provides 2,000 watts of electrical power for the life of the mission, and there is enough propellant onboard for at least 10 years of science operations.How much data will webb transmit each day?
Webb can downlink at least 57.2 gigabytes of recorded science data each day, with a maximum data rate of 28 megabits per second.Can webbs sunshield withstand micrometerial impacts?
The sunshield layers are built with ripstops included, so if something pierced a layer, it couldn't rip very far, allowing the layer to maintain structural integrity.How are webb mirrors alligned after the rigors of launch?
The primary mirror segments and secondary mirror are moved by six actuators that are attached to the backs of the mirrors. The primary segments have an additional actuator at the center of the mirror to adjust their curvature. Those seven spots are adjustable to align the 18 segments of the primary mirror to each other, and adjust the primary and secondary mirrors to the fixed tertiary mirror and the instruments.How much gold is used to make webb telescope?
A little more than 48 grams of gold are used in the Webb mirror. This is equivalent to the mass of a golf ball, which would fill a volume the size of a marble. This gold is a thin (100 nanometers) layer that is vacuum vapor deposited on each of the 18 primary mirror segments and the single secondary mirror. Gold is a highly reflective material at infrared wavelengths, helping to focus light from distant objects onto Webb’s sensitive instruments.How much of the sky can webb see?
Over the course of six months, as Webb orbits the Sun with Earth, it has the ability to observe almost any point in the sky. Webb’s field of regard is limited to a 50-degree swath of the celestial sphere: About 39% of the sky is potentially visible to Webb at any given time. Because Webb must face away from objects that are warm and close enough to interfere with its ability to observe faint infrared light, it cannot observe the Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, or the Moon.What objects webb observe first?
During its first year of science operations, Webb will observe objects in the Director's Discretionary Early Release Science program. targets from proposals from the General Observer's Cycle 1 program, and some observations selected as part of the Guaranteed Time Observations.Which wavelength can webb observe?
Webb will be able to measure light wavelengths from 0.6 to 28.8 micrometers. The capabilities of the individual instruments are:- Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam): 0.6–5 micrometers
- Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec): 0.7–5 micrometers
- Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI): 5–28.5 micrometers
- Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS/NIRISS): 0.6–5 micrometers
